|
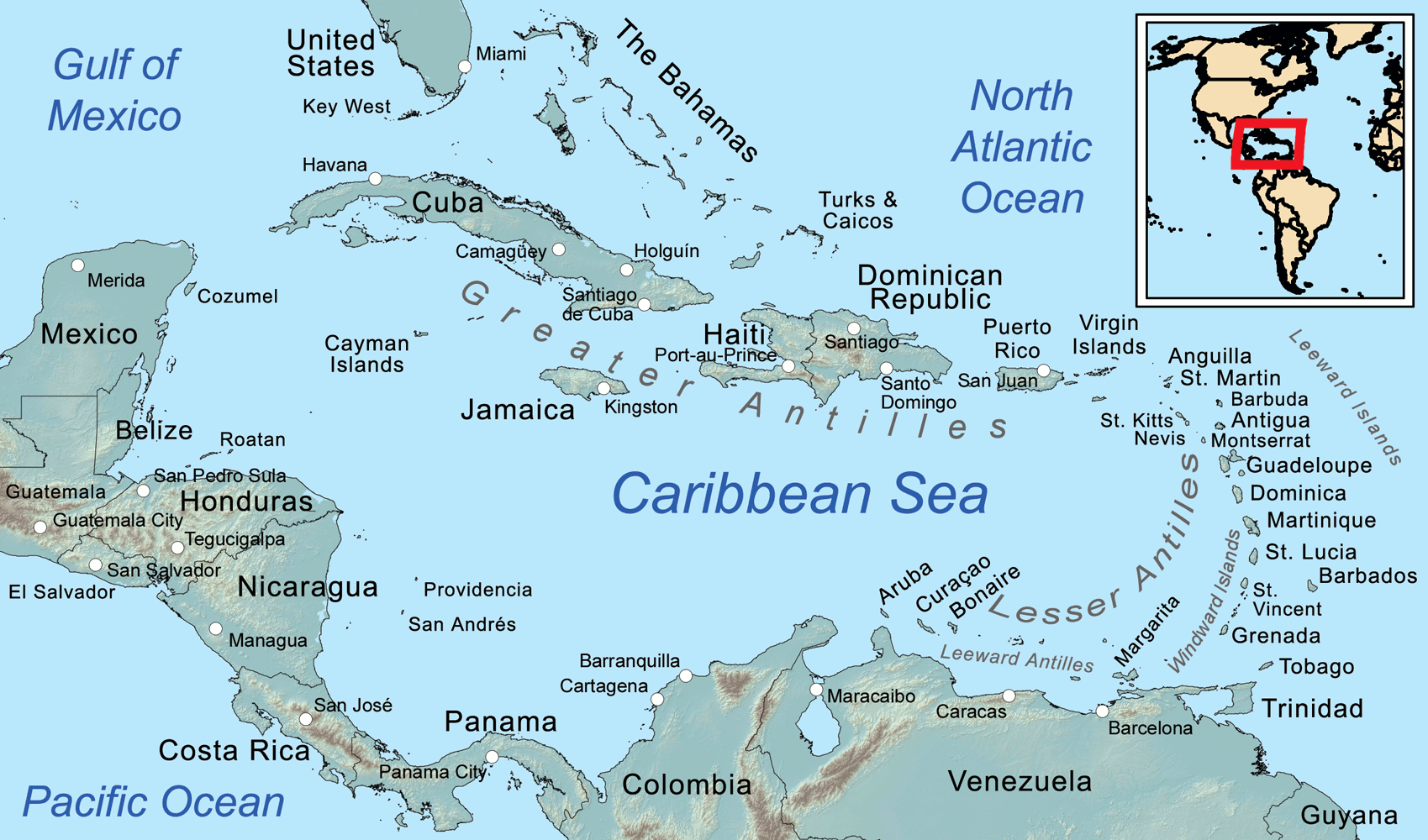
Map
of the Caribbean Sea, showing the Greater, Lesser, and Leeward Antilles, the
Leeward and Windward Islands.
With its immense cultural heritage and stunning beaches, the Dominican Republic ranks 85th overall in terms of the most populated countries in the world. You’ll find the island located on the eastern side of the Antilles, on the island of
Hispaniola. Santo Domingo and its unique cobblestoned historic centre is the largest city.
Population in 2019: 10,783,958
The economy of the Dominican Republic is the seventh largest in Latin America, and is the largest in the
Caribbean and Central American region. The Dominican Republic is an upper-middle income developing country with important sectors including mining, tourism, manufacturing (medical devices, electrical equipment, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals), energy, real estate, infrastructure, telecommunications and
agriculture. The Dominican Republic is on track to achieve its goal of becoming a high-income country by 2030, and is expected to grow 79% in this decade. The country is the site of the single largest
gold mine in Latin America, the Pueblo Viejo mine.
Although the service sector is currently the leading employer of Dominicans (due principally to growth in tourism and free-trade zones), agriculture remains an important sector in terms of the domestic market and is in second place (behind mining) in terms of export earnings. Tourism accounts for more than $7.4 billion in annual earnings in 2019. Free-trade zone earnings and tourism are the fastest-growing export sectors. A leading growth engine in the Free-trade zone sector is the production of medical equipment for export having a value-added per employee of $20,000
USD, total revenue of $1.5 billion USD, and a growth rate of 7.7% in 2019. The medical instrument export sector represents one of the highest-value added sectors of the country's economy, a true growth engine for the country's emerging market.
Remittances are an important sector of the economy, contributing $8.2 billion in 2020. Most of these funds are used to cover household expenses, such as housing, food, clothing, health care and education. Secondarily, remittances have financed businesses and productive activities. Thirdly, this combined effect has induced investment by the private sector and helps fund the public sector through its value-added tax. The combined import market including the free-trade-zones amounts to a market of $20 billion a year in 2019. The combined export sector had revenues totaling $11 billion in 2019. The consumer market is equivalent to $61 billion in 2019. An important indicator is the average commercial loan interest rate, which directs short-term investment and stimulates long-term investment in the economy. It is currently 8.30%, as of June 2021.
The Dominican Republic is the most visited destination in the
Caribbean. The year-round golf courses are major attractions. A geographically diverse nation, the Dominican Republic is home to both the Caribbean's tallest mountain peak, Pico Duarte, and the Caribbean's largest lake and lowest point, Lake Enriquillo. The island has an average temperature of 26 °C (78.8 °F) and great climatic and biological diversity. The country is also the site of the first cathedral, castle, monastery, and fortress built in the Americas, located in Santo Domingo's Colonial Zone, a World Heritage Site. Baseball is the de facto national sport.
POLITICS
Christopher Columbus arrived on the island on December 5, 1492, during the first of his four voyages to the Americas. He claimed the land for Spain and named it La Española, due to its diverse climate and terrain, which reminded him of the Spanish landscape. In 1496, Bartholomew Columbus, Christopher's brother, built the city of Santo Domingo, Western Europe's first permanent settlement in the "New World". The Spaniards created a plantation economy on the island. The colony was the springboard for the further Spanish conquest of America and for decades the headquarters of Spanish power in the hemisphere.
In 1838, Juan Pablo Duarte founded a secret society called La Trinitaria, which sought the complete independence of Santo Domingo without any foreign intervention. Also Francisco del Rosario Sánchez and Ramon Matias Mella, despite not being among the founding members of La Trinitaria, were decisive in the fight for independence. Duarte, Mella, and Sánchez are considered the three Founding Fathers of the Dominican Republic.
The Dominican Republic's first constitution was adopted on November 6, 1844. The state was commonly known as Santo Domingo in English until the early 20th century.
In 1869, U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant ordered U.S. Marines to the island for the first time. Pirates operating from Haiti had been raiding U.S. commercial shipping in the Caribbean, and Grant directed the Marines to stop them at their source. Following the virtual takeover of the island, Báez offered to sell the country to the United States. Grant desired a naval base at Samaná and also a place for resettling newly freed African Americans. The American Senate blocked the deal.
During World War II, Trujillo symbolically sided with the Allies and declared war on Japan the day after the attack on Pearl Harbor and on Nazi Germany and Italy four days later. Soon after, German U-boats torpedoed and sank two Dominican merchant vessels that Trujillo had named after himself. German U-boats also sank four Dominican-manned ships in the Caribbean. The country did not make a military contribution to the war, but Dominican sugar and other agricultural products supported the Allied war effort. American Lend-Lease and raw material purchases proved a powerful inducement in obtaining cooperation of the various Latin American republics. Over a hundred Dominicans served in the American armed forces.
In June 1960, Trujillo legalized the Communist Party and attempted to establish close political relations with the Soviet Bloc. Both the assassination attempt and the maneuver toward the Soviet Bloc provoked immediate condemnation throughout Latin America. Once its representatives confirmed Trujillo's complicity in the assassination attempt, the Organization of American States, for the first time in its history, decreed sanctions against a member state. The United States severed diplomatic relations with the Dominican Republic on August 26, 1960, and in January 1961 suspended the export of trucks, parts, crude oil, gasoline and other petroleum products. U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower also took advantage of OAS sanctions to cut drastically purchases of Dominican sugar, the country's major export. This action ultimately cost the Dominican Republic almost $22,000,000 in lost revenues at a time when its economy was in a rapid decline. Trujillo had become expendable.
On April 28, U.S. President Lyndon Johnson, concerned that communists might take over the revolt and create a "second Cuba," sent 42,000 troops into Santo Domingo, in Operation Powerpack. "We don't propose to sit here in a rocking chair with our hands folded and let the Communist set up any government in the Western Hemisphere," Johnson said.[118] The forces were soon joined by comparatively small contingents from the Organization of American States (OAS). The Loyalists used the U.S. presence to deploy its forces and attack Constitutionalists. As a result, Loyalist forces destroyed most Constitutionalist bases and captured the rebel radio station, effectively ending the war. On May 13, Loyalist forces launched Operation Limpieza and captured the northern part of Santo Domingo. Many black civilians were killed during the operation. A cease-fire was declared on May 21.
A pair of Marines barricaded behind a wall watch for snipers in Santo Domingo
The U.S. began withdrawing some of its troops by late May. However, Col. Francisco Caamaño's untrained civilians attacked American positions on June 15. Despite the coordinated attack involving mortars, rocket launchers, and several light tanks, the rebels lost a 56-square-block area to 82nd Airborne Division units which had received OAS permission to advance.
The Dominican death toll for the entire period of civil war and occupation totaled more than 3,000. A total of 44 American peacekeepers died and 283 were wounded. U.S. and OAS troops remained in the country for over a year and left after supervising elections in 1966 won by Joaquín Balaguer. He had been Trujillo's last puppet-president.
In 2003 the bankruptcy of three banking entities whose savers were protected by the government led to inflation. This caused a severe economic crisis accompanied by the devaluation of the currency and capital outflows, instability that led to the bankruptcy of many companies.
n 2008, Fernández was elected for a third term. Fernández and the PLD are credited with initiatives that have moved the country forward technologically, on the other hand, his administrations have been accused of corruption. Danilo Medina of the PLD was elected president in 2012 and re-elected in 2016, serving to 2020.
However, during his second term there were attempts to seek a third term which was frustrated after a call from the US Department of State secretary Mike Pompeo.
Medina's family, including two of his brothers, are currently being investigated under allegations of corruption, involving traffic of influence by which they benefited under Medina presidency, obtaining multiple contracts and business with the State. As of November 2020, the investigation process had entered a new phase following the arrests of two of Medina's brothers.
The pirates of yore would have felt right at home. The UK is currently
(2022) the money laundering capital of the
world. A form of corruption to equal state sanctioned piracy: privateering.
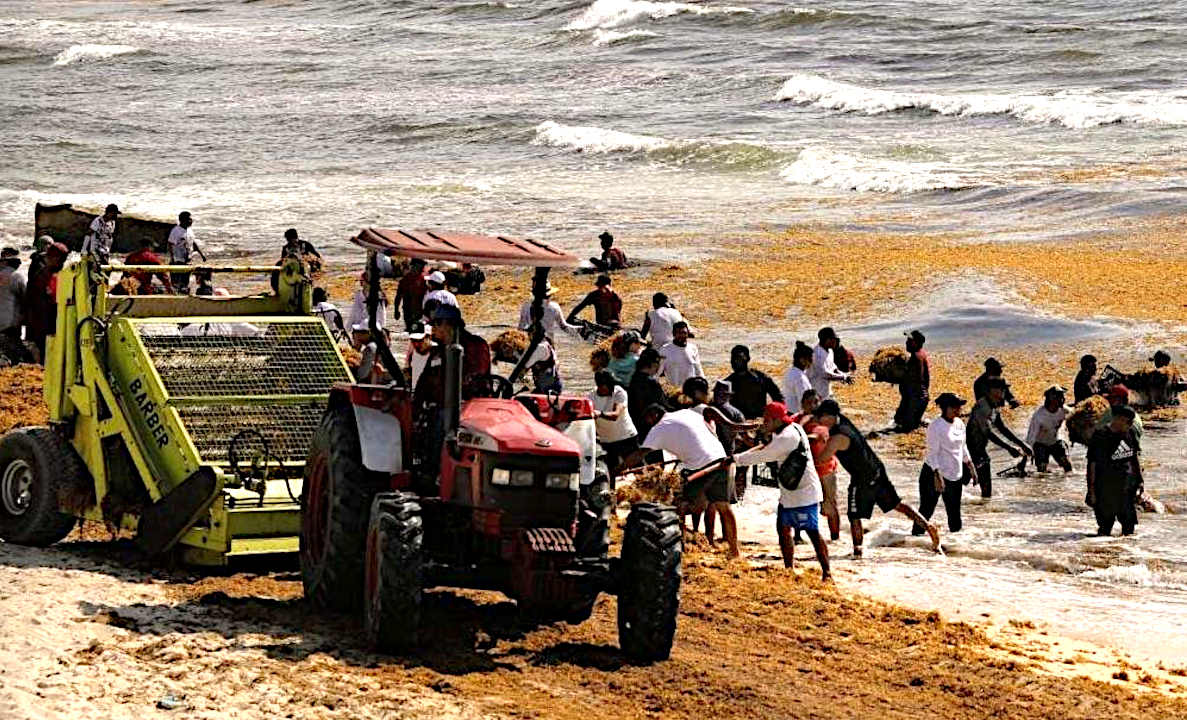

SARGASSUM:
Represents an immediate
threat to the economics of the Caribbean Islands, the
Gulf of
Mexico, and African West Coast, but is
also a potential asset if it can be economically harvested and used for,
among other things, fertilizer for agriculture: where
there is a world shortage.
BIOMASS - BUILDING
MATERIALS - CANCER
TREATMENTS - CLOTHING
& SHOES - CO2
SEQUESTRATION - COSMETICS
FERTILIZERS - FOODS - MEDICINES - MINERALS - PACKAGING - SUPPLEMENTS - VITAMINS
THE
CARIBBEAN ISLANDS BY
POPULATION
1
Cuba 11,252,999
2 Haiti
11,263,077 (Hispaniola)
3 Dominican Republic 10,766,998 (Hispaniola)
4 Puerto Rico (US) 3,508,000
5 Jamaica 2,729,000
6 Trinidad and Tobago 1,357,000
7 Guadeloupe (France) 405,000
8 Martinique (France) 383,000
9 Bahamas 379,000
10 Barbados 283,000
11 Saint Lucia 172,000
12 Curaçao (Netherlands) 157,000
13 Aruba (Netherlands) 110,000
14 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 110,000
15 United States Virgin Islands
105,000
16 Grenada 104,000
17 Antigua and Barbuda 89,000
18 Dominica 71,000
19 Cayman Islands (UK) 59,000
20 Saint Kitts and Nevis 46,000
21 Sint Maarten (Netherlands) 39,000
22 Turks and Caicos Islands (UK) 37,000
23 Saint Martin (France) 36,000
24 British Virgin Islands (UK) 31,000
25 Caribbean Netherlands
26,000
26 Anguilla (UK) 14,000
27 Saint Barthélemy (France) 10,000
28 Montserrat (UK) 5,000
29
Tortuga 25,936
30
Roatán 110,000
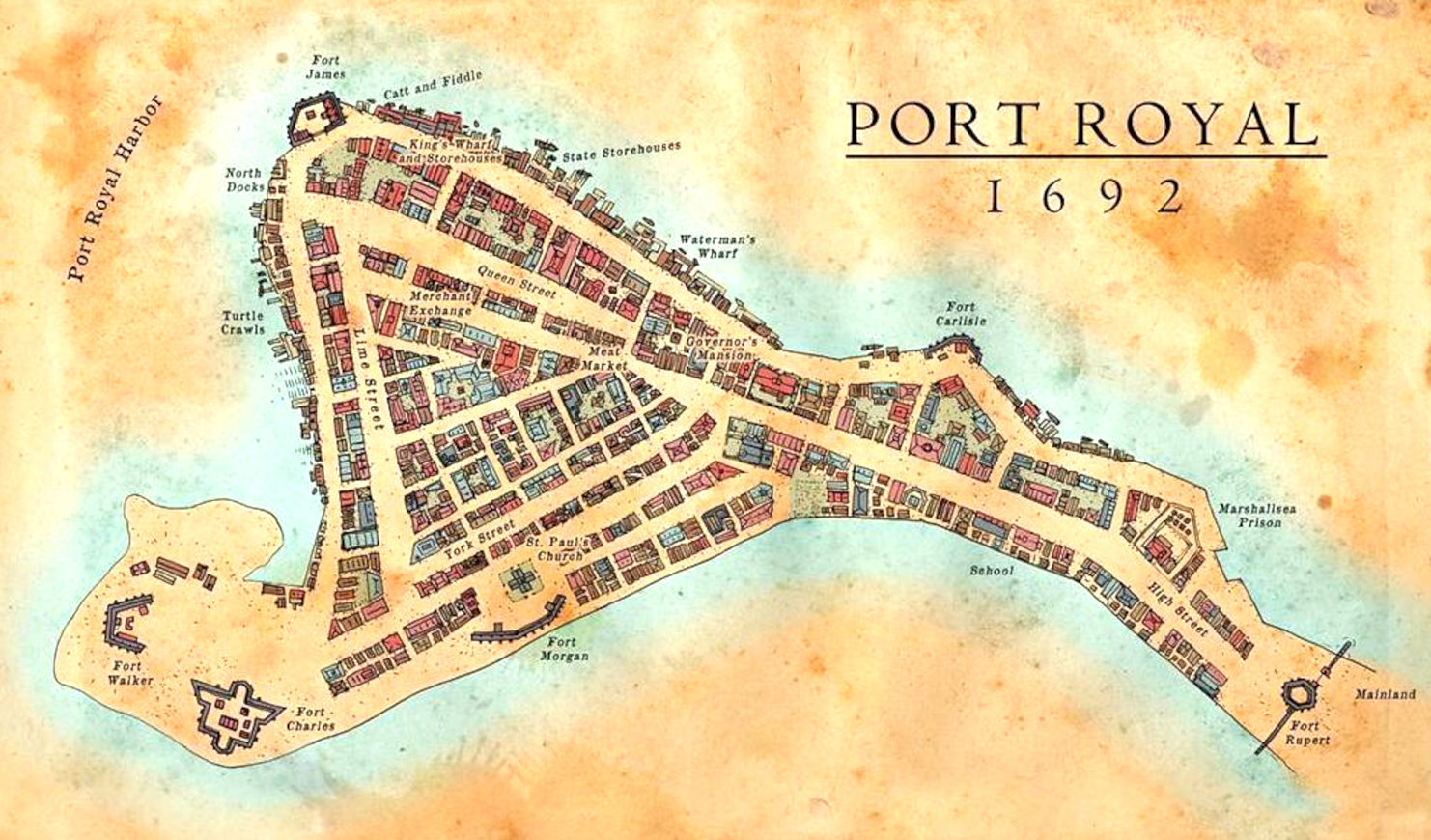
Map
of Port Royal
from 1692, where the notorious buccaneer, Sir Henry Morgan
was buried, along with a Code to give meaning a treasure Map inherited by Lord
Huntington - giving the whereabouts of a Kings ransom. Unfortunately,
Port Royal was sunk when hit by an earthquake and tsunami in June 1692,
along with the grave of the infamous buccaneer, lost in time until
re-discovered by John
Storm and the Elizabeth
Swann. This is the start of a race to find the hidden stash, involving treachery
and industrial espionage.
The
Caribbean
Sea is littered with shipwrecks and dotted with dozens of paradise
islands, where pirates
are said to have buried their treasure.
Many island nations are at risk as to rising
sea levels, caused by climate
change, with the United
Nations powerless to deal with global
warming, being dependent on fossil
fuels. The area has some of the most interesting World
Atlas locations on Planet
Earth.
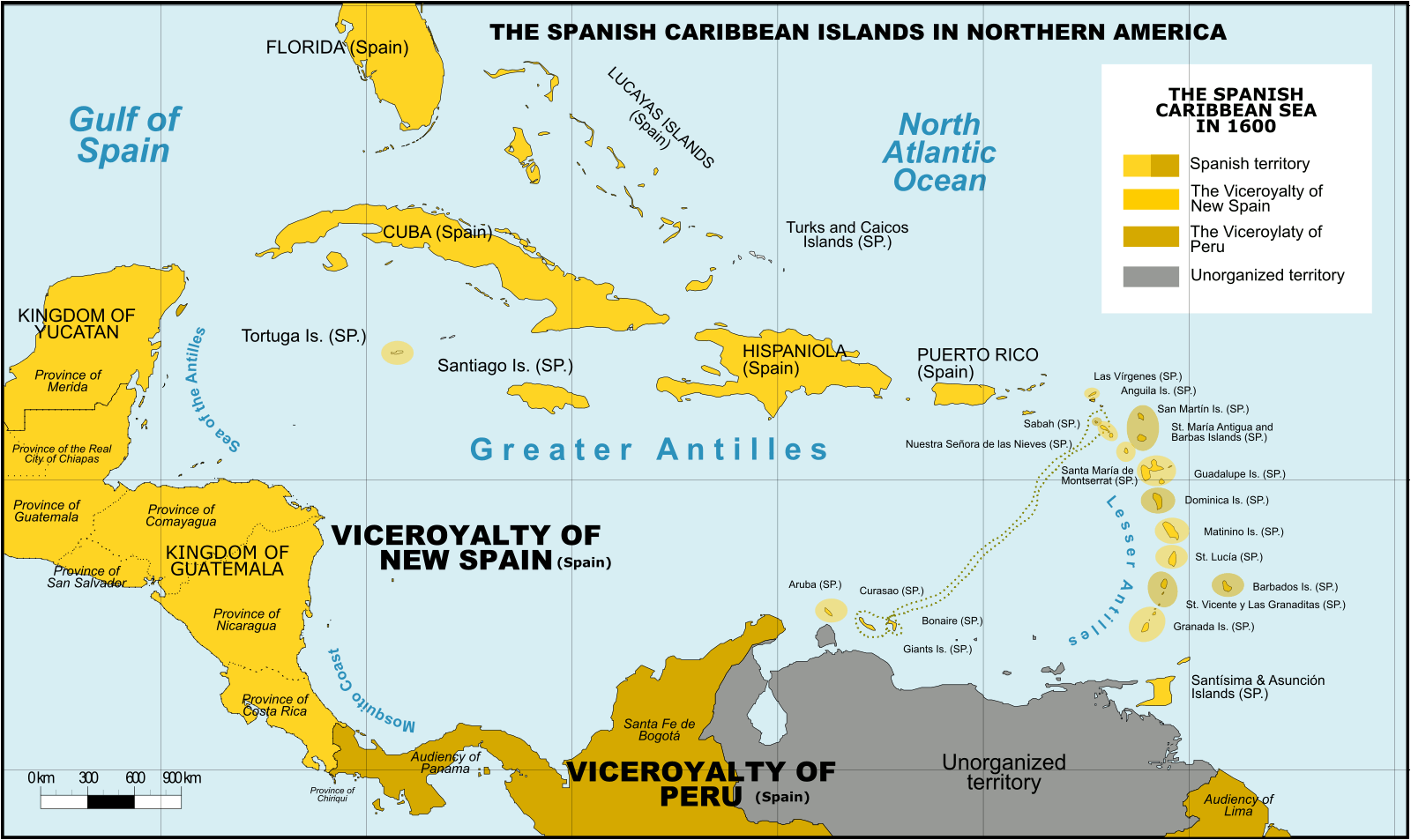
Spanish Caribbean Islands 1600 Spanish Overseas territories Northern America Turks and Caicos Islands (1492-1516, 1516-1678) * Islas Turcas y Caicos The Bahamas (1492-1516, 1516-1648) *Islas Lucayas Bermuda (1503-1516, 1516-1609) *Carabela/Isla de los Diablos Greater Antilles Cuba (1492-1762, 1763-1898) *Juana Cayman Islands (UK) (1503-1670) *Islas de las Tortugas La Española/Hispanola (1492-1795, 1801-1822) Dominican Republic (1492-1795, 1801-1822, 1861-1863) *Santo Domingo Haiti (1492-1793) *Santa María Jamaica (1492-1655) *Isla Santiago Puerto Rico (US) (1493-1898) *San Juan Bautista Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Virgin Islands (1493-1587) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes St. Thomas (US) (1493-1587) St. John (US) (1493-1587) St. Croix (US) (1493-1587) Water Island (US) (1493-1587) British Virgin Islands (UK) (1493-1648) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes Tortola (UK) (1493-1648) Virgin Gorda (UK) (1493-1672) Anegada (UK) (1493-1672) Jost Van Dyke (UK) (1493-1672) Anguilla (UK) (1500-1631, 1631-1650) *Isla de la Anguila Saint Martin/Sint Maarten (France/Neth.) (1493-1631) *San Martín Saint-Barthélemy (Fr.) (1493-1648) *San Bartolomeo Saba (Neth.) (1493-1640) *Saba/San Cristóbal Sint Eustatius (Neth.) (1493-1640) *San Eustaquio St. Kitts and Nevis (1493-1628) *Nuestra Señora de las Nieves Saint Kitts (1493-1628) *San Cristóbal Nevis (1493-1628) *Nieves Antigua and Barbuda Barbuda (1493-1628) *Santa Dulcina Antigua (1493-1632) *Santa María de la Antigua Redonda (1493-1632) *Santa María la Redonda Montserrat (UK) (1493-1632) *Santa María de Monstserrat Guadeloupe (Fr.) (1493-1631) *Santa Guadalupe Windward Islands: Dominica (1493-1635) *Domingo Martinique (Fr.) (1502-1635) *Martinino Saint Lucia (St. Lucia) (1502-1660) *Santa Lucía Barbados (1492-1620) *Los Barbados/El Barbudo St. Vincent and the Grenadines (1498-1627) *San Vicente Saint Vincent the Grenadines Grenada (1498-1650) *Concepción Carriacou & Petite Martinique (Grenada) Trinidad & Tobago (1498-1628) *Santísima e Asunción Aruba (Neth.) (1499-1648) *Aruba/Oroba Curaçao (Neth.) (1499-1634) *Curasao/Isla de los Gigantes Bonaire (Neth.) (1499-1635) * Bonaire/Buon Aire Viceroyalty of New Granada Los Roques Archipelago (Ven) La Orchila (Ven) La Tortuga (Ven) La Blanquilla (Ven) Margarita Island (Ven) Coche (Ven) Cubagua (Ven) Other islands (Ven) *Founded Spanish names
CITIES
LOST IN INNERSPACE
ATLANTIS
- MEDITERRANEAN SEA
ATLIT-YAM
- ISRAEL
BAIA
- ITALY
DWARKA
- INDIA
PAVLOPETRI
- GREECE
PHANAGORIA
- BLACK SEA
PORT
ROYAL - JAMAICA
RUNGHOLT
- DENMARK
THONIS-HERACLEION
AND ALEXANDRIA - EGYPT
YONAGUNI
JIMA - JAPAN



STUDIO/AGENTS: A draft script for
Kulo-Luna is available on request. Cleopatra The Mummy is currently under
development
|



