|
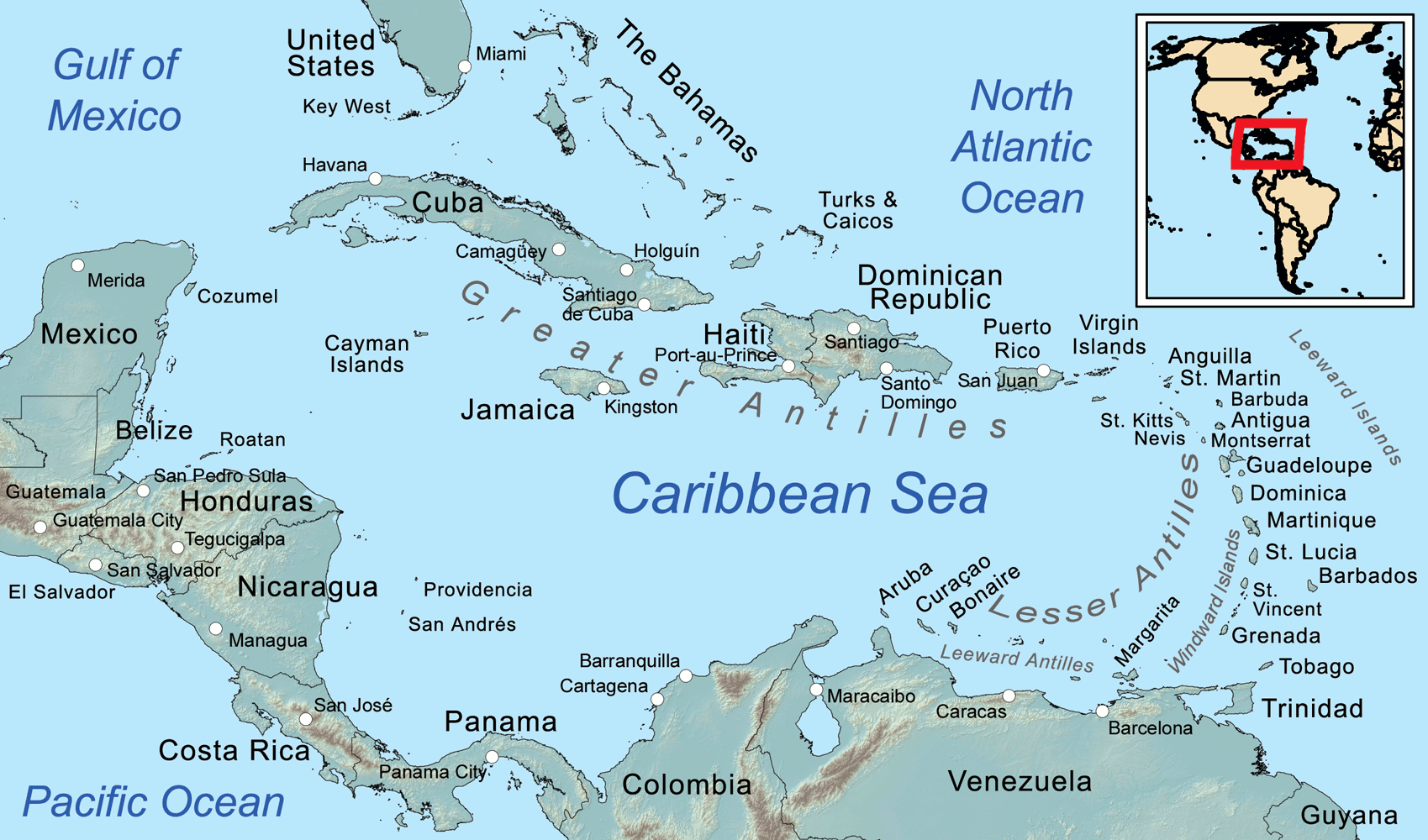
Map
of the Caribbean Sea, showing the Greater, Lesser, and Leeward Antilles, the
Leeward and Windward Islands.
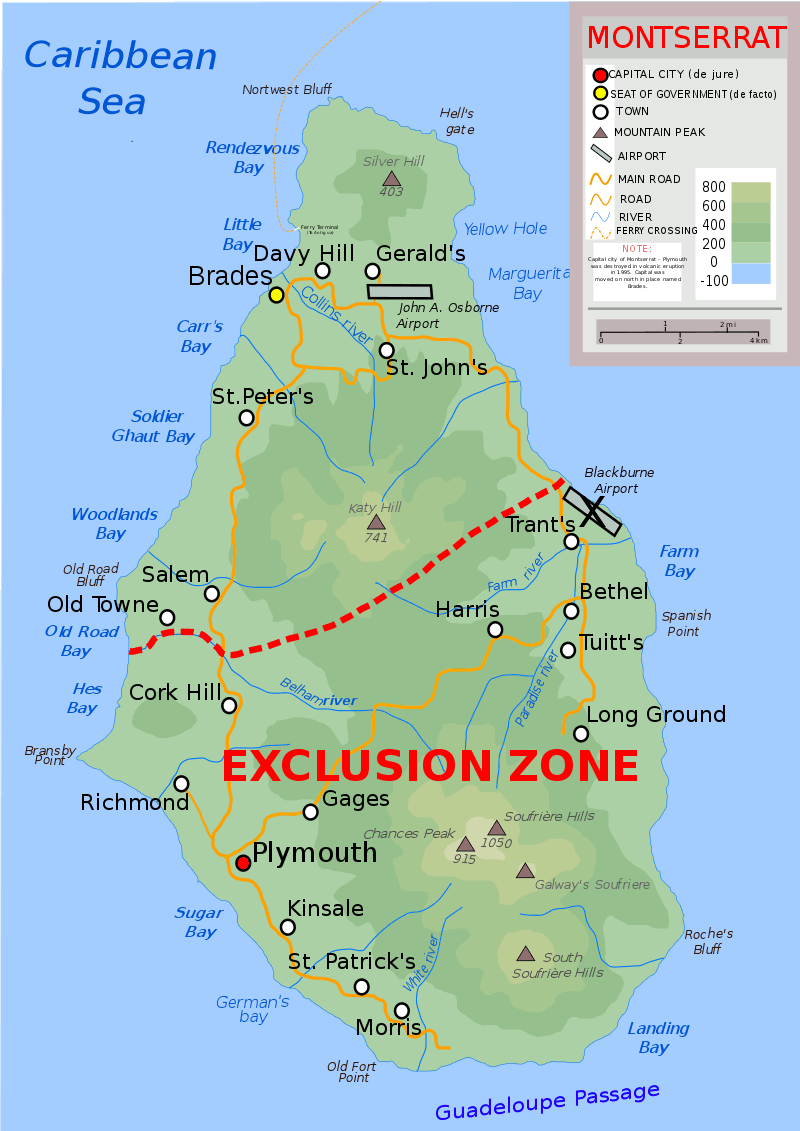
Montserrat is a British Overseas Territory in the
Caribbean. The island is in the Leeward Islands, which is part of the chain known as the Lesser Antilles, in the West Indies. Montserrat measures approximately 16 km (10 mi) in length and 11 km (7 mi) in width, with approximately 40 km (25 mi) of coastline. Montserrat is nicknamed "The Emerald Isle of the Caribbean" both for its resemblance to coastal Ireland and for the Irish ancestry of many of its inhabitants. Montserrat is the only non-fully sovereign full member of the Caribbean Community and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States.
On 18 July 1995, the previously dormant Soufrière Hills volcano, in the southern part of the island, became active. Eruptions destroyed Montserrat's Georgian era capital city of Plymouth. Between 1995 and 2000, two-thirds of the island's population was forced to flee, primarily to the United Kingdom, leaving fewer than 1200 people on the island in 1997 (rising to nearly 5000 by 2016). The volcanic activity continues, mostly affecting the vicinity of Plymouth, including its docking facilities, and the eastern side of the island around the former W. H. Bramble Airport, the remnants of which were buried by flows from volcanic activity on 11 February 2010.
An exclusion zone, encompassing the southern half of the island to as far north as parts of the Belham Valley, was imposed because of the size of the existing volcanic dome and the resulting potential for pyroclastic activity. Visitors are generally not permitted entry into the exclusion zone, but a view of the destruction of Plymouth can be seen from the top of Garibaldi Hill in Isles Bay. Relatively quiet since early 2010, the volcano continues to be closely monitored by the Montserrat Volcano Observatory.
A new town and port are being developed at Little Bay, which is on the northwest coast of the island. While this construction proceeds, the centre of government and businesses is at Brades.
In November 1493, Christopher Columbus passed Montserrat in his second voyage, after being told that the island was unoccupied due to raids by the Caribs.
A number of Irishmen settled in Montserrat in 1632. Most came from nearby Saint Kitts at the instigation of the island's governor Thomas Warner, with more settlers arriving later from
Virginia. The preponderance of Irish in the first wave of European settlers led a leading legal scholar to remark that a "nice question" is whether the original settlers took with them the law of the Kingdom of Ireland insofar as it differed from the law of the
Kingdom of England.
The Irish being historical allies of the French, especially in their dislike of the English, invited the French to claim the island in 1666, although no troops were sent by France to maintain control. However the French did attack and briefly occupy the island in the late 1660s; it was captured shortly afterwards by the English and English control of the island was confirmed under the Treaty of Breda the following year. Despite the seizing by force of the island by the English, the island's legal status is that of a "colony acquired by settlement".
POLITICS
Montserrat is an internally self-governing overseas territory of the United Kingdom. The United Nations Committee on Decolonization includes Montserrat on the
United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories. The island's head of state is
Queen Elizabeth
II, represented by an appointed Governor. Executive power is exercised by the government, whereas the Premier is the head of government. The Premier is appointed by the Governor from among the members of the Legislative Assembly which consists of nine elected members. The leader of the party with a majority of seats is usually the one who is appointed. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Legislative Assembly. The Assembly also includes two ex officio members, the attorney general and financial secretary.
Military defence is the responsibility of the United Kingdom so the island has no regular army.
ECONOMY
Montserrat's economy was devastated by the 1995 eruption and its aftermath; currently the island's operating budget is largely supplied by the British government and administered through the Department for International Development (DFID) amounting to approximately £25 million per year. Additional amounts are secured through income and property taxes, licence and other fees as well as customs duties levied on imported goods.
The limited economy of Montserrat, with a population under 5000, consumes 2.5 MW of electric power, produced by five diesel generators. Two exploratory geothermal wells have found good resources and the pad for a third geothermal well was prepared in 2016. Together the geothermal wells are expected to produce more power than the island requires. A 250 kW solar PV station was commissioned in 2019, with plans for another 750 kW.
A report published by the CIA indicates that the value of exports totalled the equivalent of US$5.7 million (2017 est.), consisting primarily of electronic components, plastic bags, apparel, hot peppers, limes, live plants and cattle. The value of imports totalled US$31.02 million (2016 est.), consisting primarily of machinery and transportation equipment, foodstuffs, manufactured goods, fuels and lubricants.
In 1979, The Beatles producer George Martin opened AIR Studios Montserrat, making the island popular with musicians who often went there to record while taking advantage of the island's climate and beautiful surroundings. In the early hours of 17 September 1989, Hurricane Hugo passed the island as a Category 4 hurricane, damaging more than 90% of the structures on the island. AIR Studios Montserrat closed, and the tourist economy was virtually wiped out. The slowly recovering tourist industry was again wiped out with the eruption of the Soufrière Hills Volcano in 1995, although it began partially to recover within fifteen years.
THE
CARIBBEAN ISLANDS BY
POPULATION
1
Cuba 11,252,999
2 Haiti
11,263,077 (Hispaniola)
3 Dominican Republic 10,766,998 (Hispaniola)
4 Puerto Rico (US) 3,508,000
5 Jamaica 2,729,000
6 Trinidad and Tobago 1,357,000
7 Guadeloupe (France) 405,000
8 Martinique (France) 383,000
9 Bahamas 379,000
10 Barbados 283,000
11 Saint Lucia 172,000
12 Curaçao (Netherlands) 157,000
13 Aruba (Netherlands) 110,000
14 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 110,000
15 United States Virgin Islands
105,000
16 Grenada 104,000
17 Antigua and Barbuda 89,000
18 Dominica 71,000
19 Cayman Islands (UK) 59,000
20 Saint Kitts and Nevis 46,000
21 Sint Maarten (Netherlands) 39,000
22 Turks and Caicos Islands (UK) 37,000
23 Saint Martin (France) 36,000
24 British Virgin Islands (UK) 31,000
25 Caribbean Netherlands
26,000
26 Anguilla (UK) 14,000
27 Saint Barthélemy (France) 10,000
28 Montserrat (UK) 5,000
29
Tortuga 25,936
30
Roatán 110,000
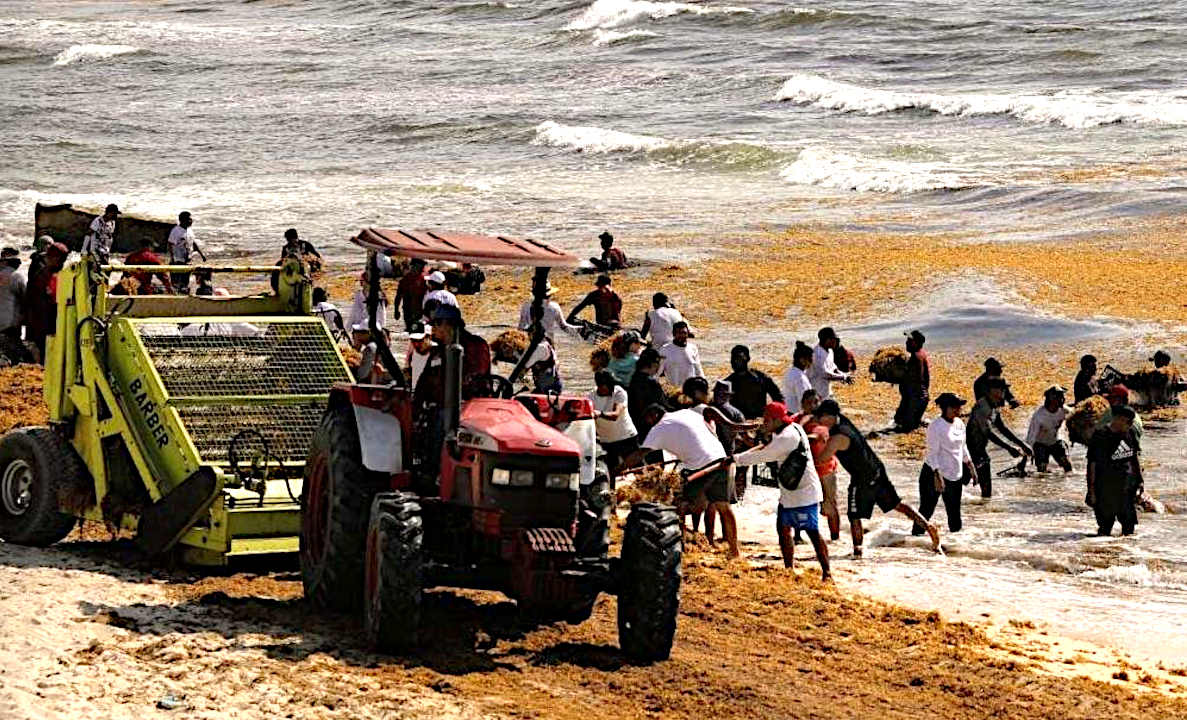

SARGASSUM:
Represents an immediate
threat to the economics of the Caribbean Islands, the
Gulf of
Mexico, and African West Coast, but is
also a potential asset if it can be economically harvested and used for,
among other things, fertilizer for agriculture: where
there is a world shortage.
BIOMASS - BUILDING
MATERIALS - CANCER
TREATMENTS - CLOTHING
& SHOES - CO2
SEQUESTRATION - COSMETICS
FERTILIZERS - FOODS - MEDICINES - MINERALS - PACKAGING - SUPPLEMENTS - VITAMINS
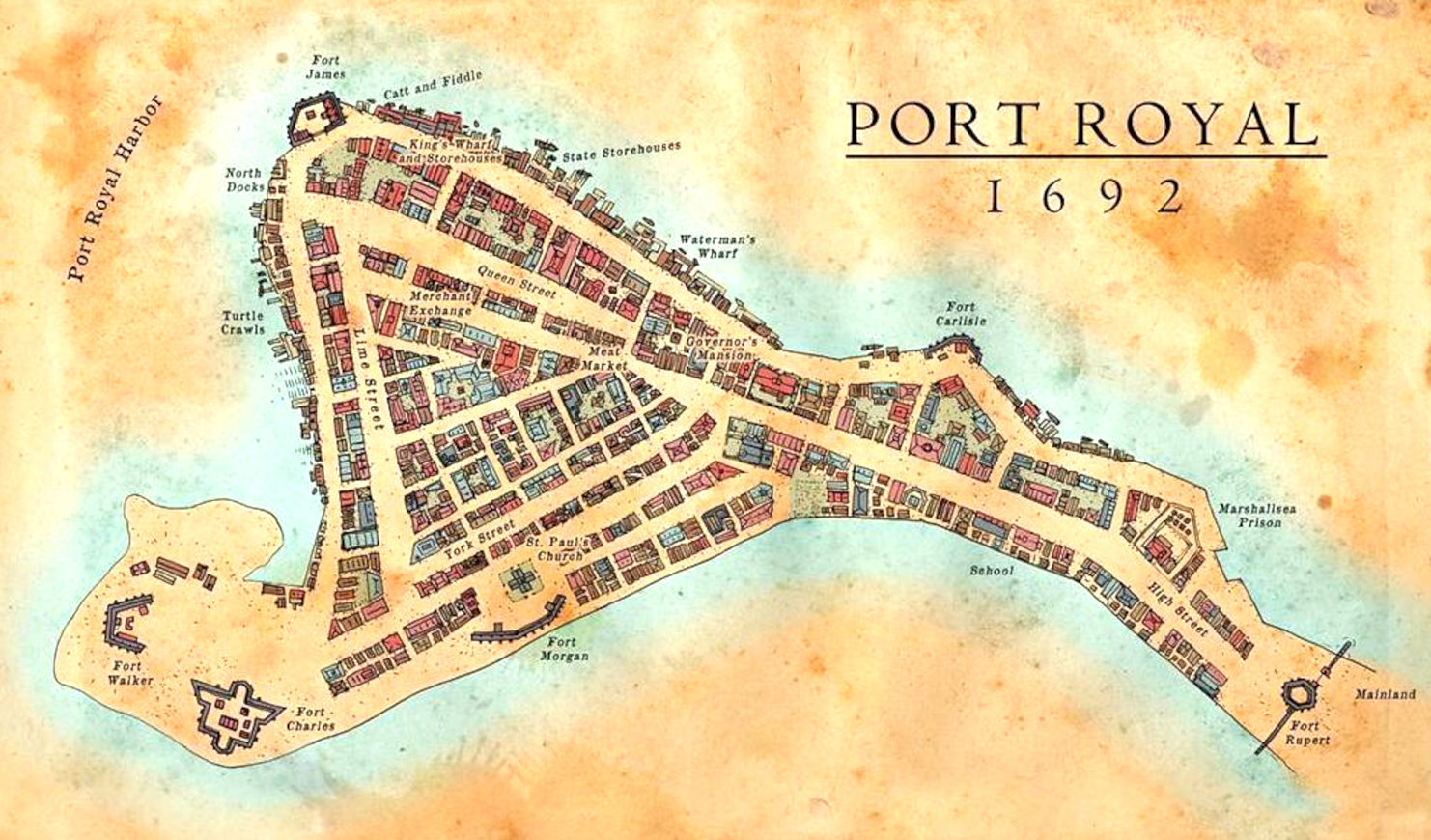
Map
of Port Royal
from 1692, where the notorious buccaneer, Sir Henry Morgan
was buried, along with a Code to give meaning a treasure Map inherited by Lord
Huntington - giving the whereabouts of a Kings ransom. Unfortunately,
Port Royal was sunk when hit by an earthquake and tsunami in June 1692,
along with the grave of the infamous buccaneer, lost in time until
re-discovered by John
Storm and the Elizabeth
Swann. This is the start of a race to find the hidden stash, involving treachery
and industrial espionage.
The
Caribbean
Sea is littered with shipwrecks and dotted with dozens of paradise
islands, where pirates
are said to have buried their treasure.
Many island nations are at risk as to rising
sea levels, caused by climate
change, with the United
Nations powerless to deal with global
warming, being dependent on fossil
fuels. The area has some of the most interesting World
Atlas locations on Planet
Earth.
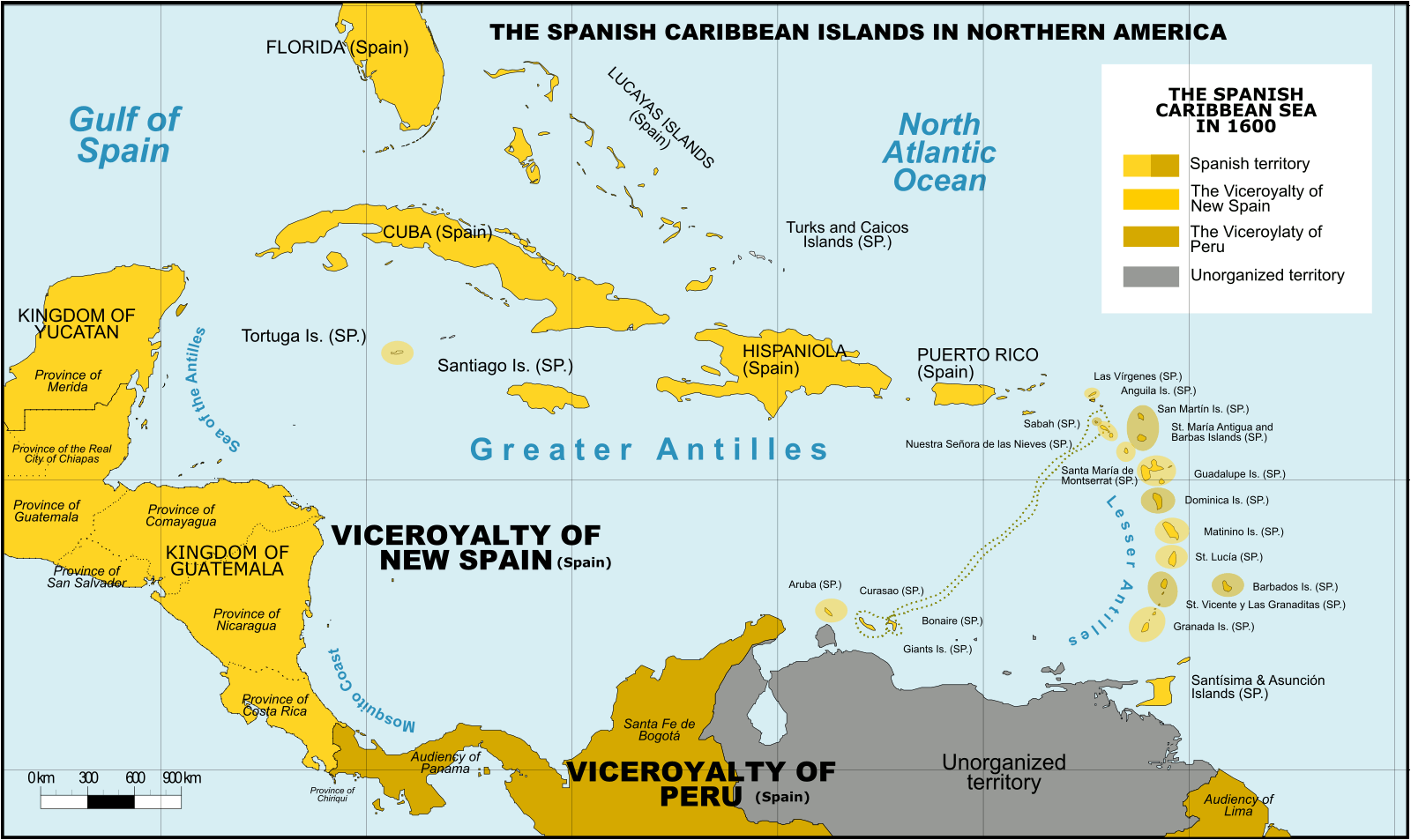
Spanish Caribbean Islands 1600 Spanish Overseas territories Northern America Turks and Caicos Islands (1492-1516, 1516-1678) * Islas Turcas y Caicos The Bahamas (1492-1516, 1516-1648) *Islas Lucayas Bermuda (1503-1516, 1516-1609) *Carabela/Isla de los Diablos Greater Antilles Cuba (1492-1762, 1763-1898) *Juana Cayman Islands (UK) (1503-1670) *Islas de las Tortugas La Española/Hispanola (1492-1795, 1801-1822) Dominican Republic (1492-1795, 1801-1822, 1861-1863) *Santo Domingo Haiti (1492-1793) *Santa María Jamaica (1492-1655) *Isla Santiago Puerto Rico (US) (1493-1898) *San Juan Bautista Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Virgin Islands (1493-1587) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes St. Thomas (US) (1493-1587) St. John (US) (1493-1587) St. Croix (US) (1493-1587) Water Island (US) (1493-1587) British Virgin Islands (UK) (1493-1648) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes Tortola (UK) (1493-1648) Virgin Gorda (UK) (1493-1672) Anegada (UK) (1493-1672) Jost Van Dyke (UK) (1493-1672) Anguilla (UK) (1500-1631, 1631-1650) *Isla de la Anguila Saint Martin/Sint Maarten (France/Neth.) (1493-1631) *San Martín Saint-Barthélemy (Fr.) (1493-1648) *San Bartolomeo Saba (Neth.) (1493-1640) *Saba/San Cristóbal Sint Eustatius (Neth.) (1493-1640) *San Eustaquio St. Kitts and Nevis (1493-1628) *Nuestra Señora de las Nieves Saint Kitts (1493-1628) *San Cristóbal Nevis (1493-1628) *Nieves Antigua and Barbuda Barbuda (1493-1628) *Santa Dulcina Antigua (1493-1632) *Santa María de la Antigua Redonda (1493-1632) *Santa María la Redonda Montserrat (UK) (1493-1632) *Santa María de Monstserrat Guadeloupe (Fr.) (1493-1631) *Santa Guadalupe Windward Islands: Dominica (1493-1635) *Domingo Martinique (Fr.) (1502-1635) *Martinino Saint Lucia (St. Lucia) (1502-1660) *Santa Lucía Barbados (1492-1620) *Los Barbados/El Barbudo St. Vincent and the Grenadines (1498-1627) *San Vicente Saint Vincent the Grenadines Grenada (1498-1650) *Concepción Carriacou & Petite Martinique (Grenada) Trinidad & Tobago (1498-1628) *Santísima e Asunción Aruba (Neth.) (1499-1648) *Aruba/Oroba Curaçao (Neth.) (1499-1634) *Curasao/Isla de los Gigantes Bonaire (Neth.) (1499-1635) * Bonaire/Buon Aire Viceroyalty of New Granada Los Roques Archipelago (Ven) La Orchila (Ven) La Tortuga (Ven) La Blanquilla (Ven) Margarita Island (Ven) Coche (Ven) Cubagua (Ven) Other islands (Ven) *Founded Spanish names
CITIES
LOST IN INNERSPACE
ATLANTIS
- MEDITERRANEAN SEA
ATLIT-YAM
- ISRAEL
BAIA
- ITALY
DWARKA
- INDIA
PAVLOPETRI
- GREECE
PHANAGORIA
- BLACK SEA
PORT
ROYAL - JAMAICA
RUNGHOLT
- DENMARK
THONIS-HERACLEION
AND ALEXANDRIA - EGYPT
YONAGUNI
JIMA - JAPAN
ISLAND
NATIONS UNDER THREAT OF SINKING
Cabo
Verde, Republic of
Carteret
Islands
Fiji,
Republic of
Hawaii
Japan
Kiribati
Maldives
Marshall
Islands, Republic of the
Micronesia,
Federated
States of
Palau
Sarichef
Island
Seychelles
Solomon
Islands
Tangier
Island
Torres
Strait Islands
Tuvalu



STUDIO/AGENTS: A draft script for
Kulo-Luna is available on request. Cleopatra The Mummy is currently under
development
|





