|
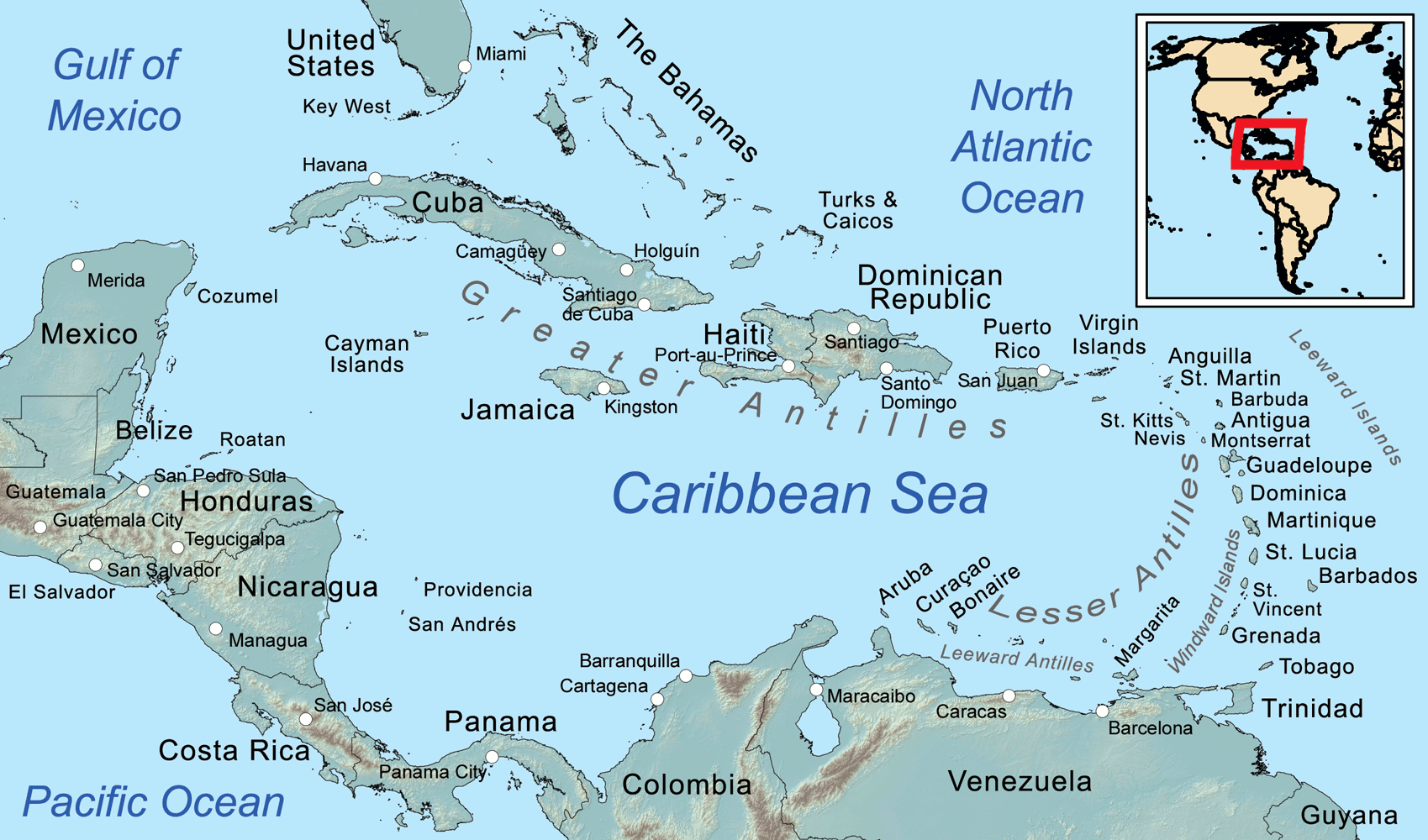
Map
of the Caribbean Sea, showing the Greater, Lesser, and Leeward Antilles, the
Leeward and Windward Islands.
Christopher Columbus was an Italian explorer and navigator who completed four voyages across the
Atlantic
Ocean, opening the way for the widespread European exploration and colonization of the Americas. His expeditions, sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, were the first European contact with the Caribbean, Central America, and South America.
The name Christopher Columbus is the Anglicisation of the Latin Christophorus Columbus. Scholars generally agree that Columbus was born in the Republic of Genoa and spoke a dialect of Ligurian as his first language. He went to sea at a young age and travelled widely, as far north as the British Isles and as far south as what is now Ghana. He married Portuguese noblewoman Filipa Moniz Perestrelo and was based in Lisbon for several years, but later took a Castilian mistress, Beatriz Enríquez de Arana; he had one son with each woman.
Largely self-educated, Columbus was widely read in geography, astronomy, and history. He developed a plan to seek a western sea passage to the East Indies, hoping to profit from the lucrative spice trade. Following Columbus's persistent lobbying in multiple kingdoms, the Catholic Monarchs Queen Isabella I and King Ferdinand II agreed to sponsor a journey west. Columbus left Castile in August 1492 with three ships and made landfall in the Americas on 12 October, ending the period of human habitation in the Americas now referred to as the pre-Columbian era. His landing place was an island in the Bahamas, known by its native inhabitants as Guanahani. He subsequently visited the islands now known as Cuba and Hispaniola, establishing a colony in what is now Haiti. Columbus returned to Castile in early 1493, bringing a number of captured natives with him. Word of his voyage soon spread throughout Europe.
Columbus made three further voyages to the Americas, exploring the Lesser Antilles in 1493, Trinidad and the northern coast of South America in 1498, and the eastern coast of Central America in 1502. Many of the names he gave to geographical features, particularly islands, are still in use. He also gave the name indios ("Indians") to the indigenous peoples he encountered. The extent to which he was aware that the Americas were a wholly separate landmass is uncertain; he never clearly renounced his belief that he had reached the Far East. As a colonial governor, Columbus was accused by his contemporaries of significant brutality and was soon removed from the post. Columbus's strained relationship with the Crown of Castile and its appointed colonial administrators in America led to his arrest and removal from Hispaniola in 1500, and later to protracted litigation over the perquisites that he and his heirs claimed were owed to them by the crown.
Columbus's expeditions inaugurated a period of exploration, conquest, and colonization that lasted for centuries, helping create the modern Western world. The transfers between the Old World and New World that followed his first voyage are known as the Columbian exchange. Columbus was widely celebrated in the centuries after his death, but public perception has fractured in the 21st century as scholars have given greater attention to the harms committed under his governance, particularly the beginning of the depopulation of Hispaniola's indigenous Taínos caused by mistreatment and Old World diseases, as well as by that people's enslavement. Proponents of the Black Legend theory of historiography claim that Columbus has been unfairly maligned as part of a wider anti-Catholic sentiment. Many places in the Western Hemisphere bear his name, including the country of Colombia, the District of Columbia, and British Columbia.
QUEST FOR FUNDING
By about 1484, Columbus proposed his planned voyage to King John II of Portugal. The king submitted Columbus's proposal to his advisors, who rejected it, correctly, on the grounds that Columbus's estimate for a voyage of 2,400 nautical miles was only a quarter of what it should have been. In 1488, Columbus again appealed to the court of Portugal, and John II again granted him an audience. That meeting also proved unsuccessful, in part because not long afterwards Bartolomeu Dias returned to Portugal with news of his successful rounding of the southern tip of Africa (near the
Cape of Good
Hope).
Columbus sought an audience with the monarchs Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile, who had united several kingdoms in the Iberian Peninsula by marrying and were now ruling together. On 1 May 1486, permission having been granted, Columbus presented his plans to Queen Isabella, who, in turn, referred it to a committee. The learned men of Spain, like their counterparts in Portugal, replied that Columbus had grossly underestimated the distance to Asia. They pronounced the idea impractical and advised the Catholic Monarchs to pass on the proposed venture. To keep Columbus from taking his ideas elsewhere, and perhaps to keep their options open, the sovereigns gave him an allowance, totaling about 14,000 maravedis for the year, or about the annual salary of a sailor. In May 1489, the queen sent him another 10,000 maravedis, and the same year the monarchs furnished him with a letter ordering all cities and towns under their dominion to provide him food and lodging at no cost.
Columbus also dispatched his brother Bartolomeo to the court of Henry VII of England to inquire whether the English crown might sponsor his expedition, but he was captured by pirates en route, and only arrived in early 1491. By that time, Columbus had retreated to La Rábida Friary, where the Spanish crown sent him 20,000 maravedis to buy new clothes and instructions to return to the Spanish court for renewed discussions.
SPAIN AGREES
Christopher
Columbus waited at King Ferdinand's camp until Ferdinand and Isabella conquered Granada, the last Muslim stronghold on the Iberian Peninsula, in January 1492. A council led by Isabella's confessor, Hernando de Talavera, found Columbus's proposal to reach the Indies implausible. Columbus had left for France when Ferdinand intervened, first sending Talavera and Bishop Diego Deza to appeal to the queen. Isabella was finally convinced by the king's clerk Luis de Santángel, who argued that Columbus would take his ideas elsewhere, and offered to help arrange the funding. Isabella then sent a royal guard to fetch Columbus, who had traveled 2 leagues (over 10 kilometers) toward Córdoba.
In the April 1492 "Capitulations of Santa Fe", King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella promised Columbus that if he succeeded he would be given the rank of Admiral of the Ocean Sea and appointed Viceroy and Governor of all the new lands he might claim for Spain. He had the right to nominate three persons, from whom the sovereigns would choose one, for any office in the new lands. He would be entitled to 10% (diezmo) of all the revenues from the new lands in perpetuity. He also would have the option of buying one-eighth interest in any commercial venture in the new lands, and receive one-eighth (ochavo) of the profits.
In 1500, during his third voyage to the Americas, Columbus was arrested and dismissed from his posts. He and his sons, Diego and Fernando, then conducted a lengthy series of court cases against the Castilian crown, known as the pleitos colombinos, alleging that the Crown had illegally reneged on its contractual obligations to Columbus and his heirs. The Columbus family had some success in their first litigation, as a judgment of 1511 confirmed Diego's position as viceroy but reduced his powers. Diego resumed litigation in 1512, which lasted until 1536, and further disputes initiated by heirs continued until 1790.
Columbus
was lucky he did not live in England between 1985-2022, here they would have
framed him for a crime and prevented any kind of appeal, reaching any court,
with further threats of harassment and imprisonment should he try to seek
justice.
JAMAICA
SHIPWRECK
Christopher Columbus was the first European to see Jamaica, claiming the island for Spain after landing there in 1494 on his second voyage to the Americas. His probable landing point was Dry Harbour, called Discovery Bay, and St. Ann's Bay was named "Saint Gloria" by Columbus, as the first sighting of the land. He later returned in 1503; however, he was shipwrecked and he and his crew were forced to live on Jamaica for a year while waiting to be rescued.
THE
CARIBBEAN ISLANDS BY
POPULATION
1
Cuba 11,252,999
2 Haiti
11,263,077 (Hispaniola)
3 Dominican Republic 10,766,998 (Hispaniola)
4 Puerto Rico (US) 3,508,000
5 Jamaica 2,729,000
6 Trinidad and Tobago 1,357,000
7 Guadeloupe (France) 405,000
8 Martinique (France) 383,000
9 Bahamas 379,000
10 Barbados 283,000
11 Saint Lucia 172,000
12 Curaçao (Netherlands) 157,000
13 Aruba (Netherlands) 110,000
14 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 110,000
15 United States Virgin Islands
105,000
16 Grenada 104,000
17 Antigua and Barbuda 89,000
18 Dominica 71,000
19 Cayman Islands (UK) 59,000
20 Saint Kitts and Nevis 46,000
21 Sint Maarten (Netherlands) 39,000
22 Turks and Caicos Islands (UK) 37,000
23 Saint Martin (France) 36,000
24 British Virgin Islands (UK) 31,000
25 Caribbean Netherlands
26,000
26 Anguilla (UK) 14,000
27 Saint Barthélemy (France) 10,000
28 Montserrat (UK) 5,000
29
Tortuga 25,936
30
Roatán 110,000
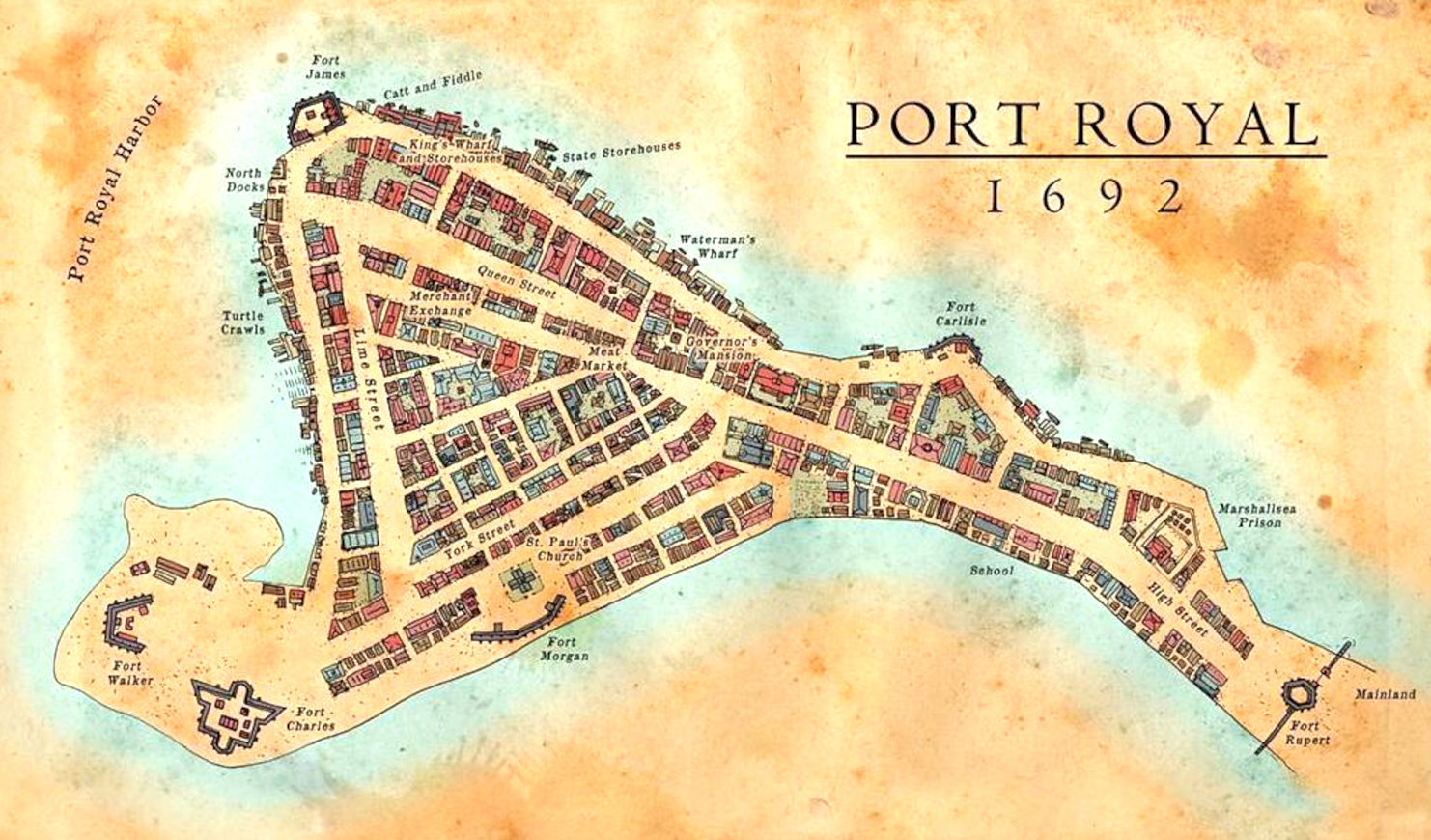
Map
of Port Royal
from 1692, where the notorious buccaneer, Sir Henry Morgan
was buried, along with a Code to give meaning a treasure Map inherited by Lord
Huntington - giving the whereabouts of a Kings ransom. Unfortunately,
Port Royal was sunk when hit by an earthquake and tsunami in June 1692,
along with the grave of the infamous buccaneer, lost in time until
re-discovered by John
Storm and the Elizabeth
Swann. This is the start of a race to find the hidden stash, involving treachery
and industrial espionage.
The
Caribbean
Sea is littered with shipwrecks and dotted with dozens of paradise
islands, where pirates
are said to have buried their treasure.
Many island nations are at risk as to rising
sea levels, caused by climate
change, with the United
Nations powerless to deal with global
warming, being dependent on fossil
fuels.
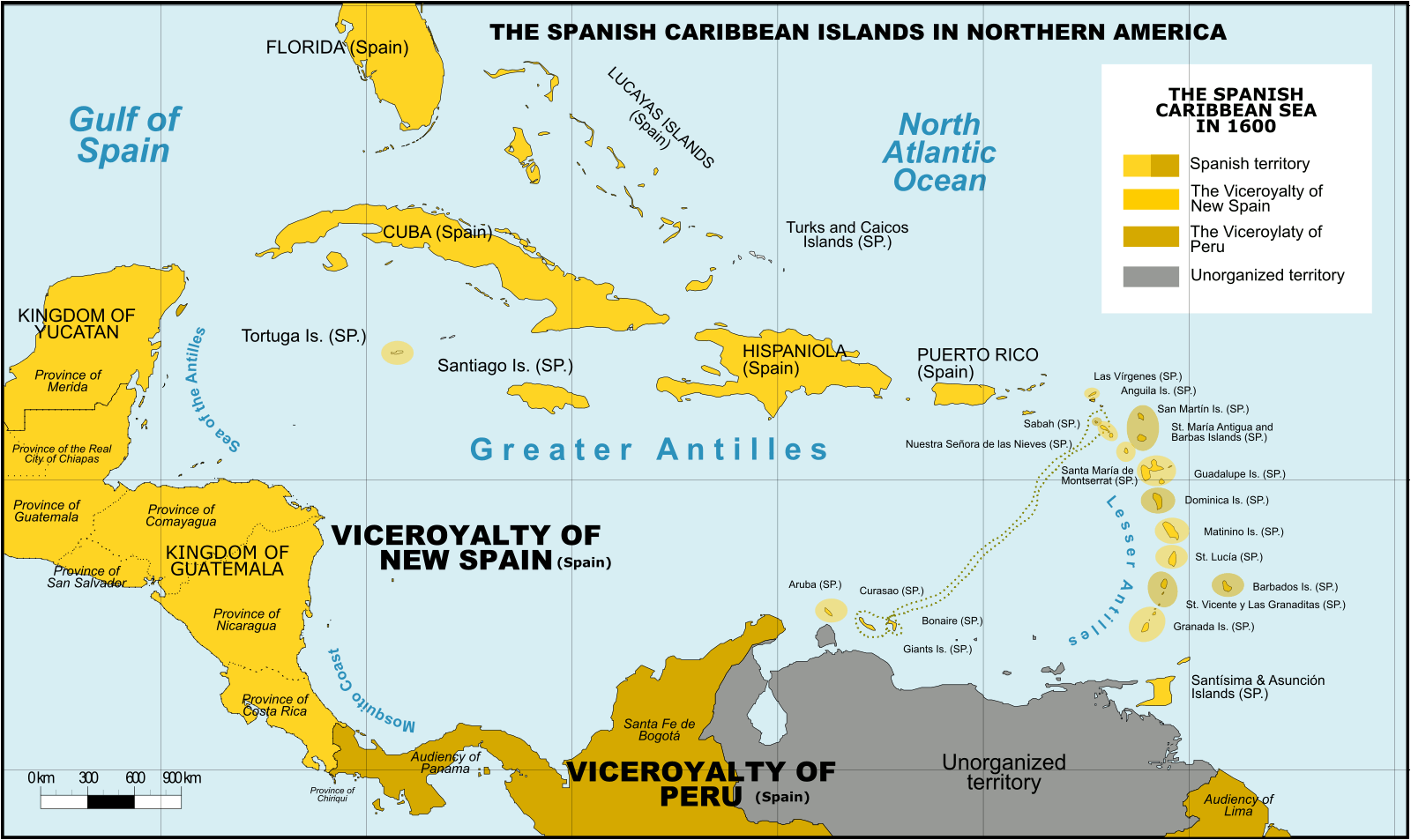
Spanish Caribbean Islands 1600 Spanish Overseas territories Northern America Turks and Caicos Islands (1492-1516, 1516-1678) * Islas Turcas y Caicos The Bahamas (1492-1516, 1516-1648) *Islas Lucayas Bermuda (1503-1516, 1516-1609) *Carabela/Isla de los Diablos Greater Antilles Cuba (1492-1762, 1763-1898) *Juana Cayman Islands (UK) (1503-1670) *Islas de las Tortugas La Española/Hispanola (1492-1795, 1801-1822) Dominican Republic (1492-1795, 1801-1822, 1861-1863) *Santo Domingo Haiti (1492-1793) *Santa María Jamaica (1492-1655) *Isla Santiago Puerto Rico (US) (1493-1898) *San Juan Bautista Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Virgin Islands (1493-1587) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes St. Thomas (US) (1493-1587) St. John (US) (1493-1587) St. Croix (US) (1493-1587) Water Island (US) (1493-1587) British Virgin Islands (UK) (1493-1648) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes Tortola (UK) (1493-1648) Virgin Gorda (UK) (1493-1672) Anegada (UK) (1493-1672) Jost Van Dyke (UK) (1493-1672) Anguilla (UK) (1500-1631, 1631-1650) *Isla de la Anguila Saint Martin/Sint Maarten (France/Neth.) (1493-1631) *San Martín Saint-Barthélemy (Fr.) (1493-1648) *San Bartolomeo Saba (Neth.) (1493-1640) *Saba/San Cristóbal Sint Eustatius (Neth.) (1493-1640) *San Eustaquio St. Kitts and Nevis (1493-1628) *Nuestra Señora de las Nieves Saint Kitts (1493-1628) *San Cristóbal Nevis (1493-1628) *Nieves Antigua and Barbuda Barbuda (1493-1628) *Santa Dulcina Antigua (1493-1632) *Santa María de la Antigua Redonda (1493-1632) *Santa María la Redonda Montserrat (UK) (1493-1632) *Santa María de Monstserrat Guadeloupe (Fr.) (1493-1631) *Santa Guadalupe Windward Islands: Dominica (1493-1635) *Domingo Martinique (Fr.) (1502-1635) *Martinino Saint Lucia (St. Lucia) (1502-1660) *Santa Lucía Barbados (1492-1620) *Los Barbados/El Barbudo St. Vincent and the Grenadines (1498-1627) *San Vicente Saint Vincent the Grenadines Grenada (1498-1650) *Concepción Carriacou & Petite Martinique (Grenada) Trinidad & Tobago (1498-1628) *Santísima e Asunción Aruba (Neth.) (1499-1648) *Aruba/Oroba Curaçao (Neth.) (1499-1634) *Curasao/Isla de los Gigantes Bonaire (Neth.) (1499-1635) * Bonaire/Buon Aire Viceroyalty of New Granada Los Roques Archipelago (Ven) La Orchila (Ven) La Tortuga (Ven) La Blanquilla (Ven) Margarita Island (Ven) Coche (Ven) Cubagua (Ven) Other islands (Ven) *Founded Spanish names
CITIES
LOST IN INNERSPACE
ATLANTIS
- MEDITERRANEAN SEA
ATLIT-YAM
- ISRAEL
BAIA
- ITALY
DWARKA
- INDIA
PAVLOPETRI
- GREECE
PHANAGORIA
- BLACK SEA
PORT
ROYAL - JAMAICA
RUNGHOLT
- DENMARK
THONIS-HERACLEION
AND ALEXANDRIA - EGYPT
YONAGUNI
JIMA - JAPAN



STUDIO/AGENTS: A draft script for
Kulo-Luna is available on request. Cleopatra The Mummy is currently under
development
|


