|
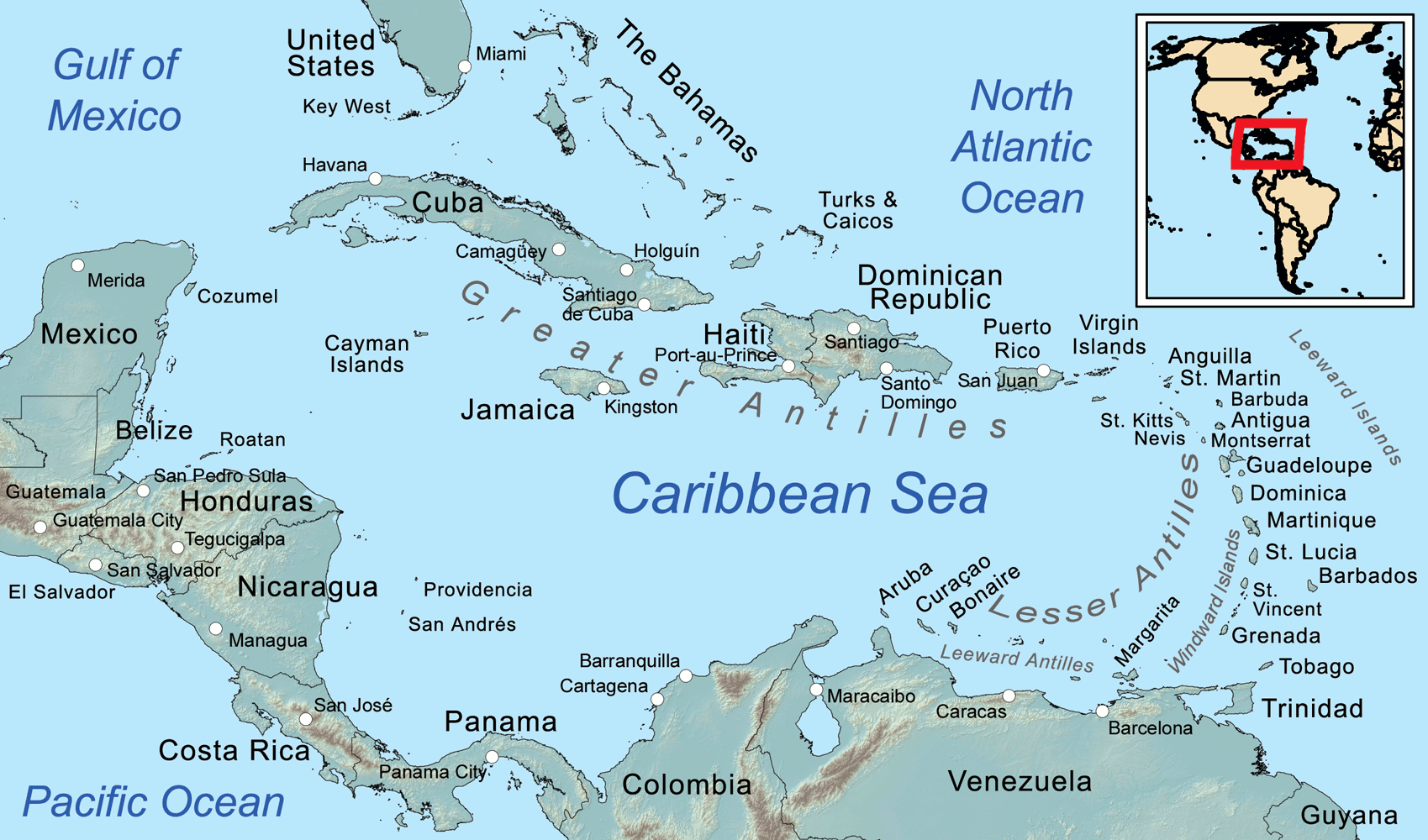
Map
of the Caribbean Sea, showing the Greater, Lesser, and Leeward Antilles, the
Leeward and Windward Islands.
Roatán is an island in the Caribbean, about 65 kilometres (40 mi) off the northern coast of Honduras. It is located between the islands of Útila and Guanaja, and is the largest of the Bay Islands of Honduras. The island was formerly known in English as Ruatan and Rattan.
It is approximately 77 kilometres (48 mi) long, and less than 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) across at its widest point. The island consists of two municipalities: José Santos Guardiola in the east and Roatán, including the Cayos Cochinos, further south in the west.
The island rests on an exposed ancient coral reef, rising to about 270 metres (890 ft) above sea level. Offshore reefs offer opportunities for diving. Most habitation is in the western half of the island.
Roatán contains a special economic zone “Zona de Empleo y de Desarrollo Económico” (ZEDE) or Zone for Economic Development and Employment, designated by Honduran constitutional provisions and legislation. The goal is to enable stable legal structures, physical environment, human rights, and taxation in order to encourage investment, migration, and economic development. This is the location of the private charter city of Próspera.
CONSERVATION
All reef systems throughout the Bay Islands are protected by the local and central government with help from charitable donations and those on the front line. Through local donations to the Marine Park and the many causes along with a concerted effort from the resorts on the island weekly clean-ups are undertaken to insure no metals or plastics litter the reef system and beaches as well as all major dive shops doing clean-ups on most of their daily dives. There are still obstacles to be defeated but the Islanders and expatriates living on the islands have taken a united stand to conserve and educate.
MARINE PARK
The Roatán Marine Park (RMP) is a grassroots, community-based, non-profit organization located on Roatán. The organization was formed in January 2005 when a group of concerned dive operators and local businesses united in an effort to protect Roatán's fragile coral reefs. Initially, the RMP's goal was to run a patrol program within the Sandy Bay-West End Marine Reserve (SBWEMR), to prevent over exploitation through unsustainable fishing practices. Over time, the organisation expanded the scope of their environmental efforts through the addition of other programs to protect Roatán's natural resources, including patrols and infrastructure, education, conservation and public awareness.
The East End Chapter of the Roatan Marine Park was created in late 2017 in an effort to expand the RMP's efforts across the entire island. The initiative and volunteer efforts saw an increase in fish coverage and a 200% increase in turtle nesting for the 2019 season, and new goals include expanding education outreach and local alternative livelihood programs.
The Roatán Marine Park was the main force behind introducing recycling to the Island as well as the popular
"Coastal clean
up" projects that have become very popular among schools, residents and expatriate communities on the Island. The Marine Park is led by a team of professional divers, marine biologists and oceanographers. In 2019 the local government passed a law banning the use and sale of
plastic
bags, bottles, containers and styrofoam. The Island expects to continue passing comprehensive environmental and pollution reforms through 2020 and beyond.
INSTITUTE OF MARINE SCIENCE
The Roatán Institute for Marine Sciences (RIMS) was established in 1989 with the primary objective being the preservation of Roatán's natural resources through education and research. RIMS is located in Sandy Bay, specifically in Anthony's Key Resort, on the northwest coast of Roatán with over 50 kilometres (30 miles) of fringing and barrier reefs, seagrass beds, mangroves, and shoreline. Over the past twenty five years, RIMS has established itself as a teaching institution and is visited by colleges as well as universities from abroad to study nearby tropical marine ecosystems and the bottlenose dolphins kept by the facility.
HISTORY
The Indians of the Bay Islands are believed to have been related to either the Paya, the Maya, the Lenca or the Jicaque, which were the tribes present on the mainland. Christopher Columbus on his fourth voyage (1502–1504) came to the islands as he visited the neighbouring Bay Island of Guanaja. Soon after, the Spanish began trading in the islands for slave labour. More devastating for the local Indians was exposure to Eurasian infectious diseases to which they had no immunity, such as smallpox and measles. No indigenous people survived the consequent epidemics.
Throughout European colonial, the Bay of Honduras attracted an array of individual settlers, pirates, traders and military forces. Various economic activities were engaged in and political struggles played out between the European powers, chiefly Britain and
Spain. Sea travellers frequently stopped over at Roatán and the other islands as resting points. On several occasions, the islands were subject to military occupation. In contesting with the Spanish for colonisation of the
Caribbean, the English occupied the Bay Islands on and off between 1550 and 1700. During this time, buccaneers found the vacated, mostly unprotected islands a haven for safe harbour and transport. English, French and Dutch pirates established settlements on the islands. They frequently raided the Spanish treasure ships, cargo vessels carrying gold and silver from the New World to Spain. In 1722 fisherman Philip Ashton was captured by the pirate Edward Low and managed to escape on a watering rendezvous on Roatan. His noted account of his subsequent year spent on the uninhabited island over the next year provides a glimpse of the island after the eradication of the Paya and before colonisation.
During the War of the Austrian Succession, a British Army detachment under the command of John Caulfeild garrisoned the island from 1742 to 1749. The garrison originally consisted of two companies of Gooch's American Regiment, but these were eventually amalgamated into the 49th Regiment of Foot (later amalgamated as part of the Cardwell Reforms into the Royal Berkshire Regiment).
In 1797, the British defeated the Garifuna, who had been supported by the French, in a conflict for control of the Windward Caribbean island of St. Vincent as part of the Second Carib War. The British then deported the Garifuna to Roatán. The majority of the Garifuna migrated to Trujillo on mainland Honduras, but a portion remained to found the community of Punta Gorda on the northern coast of Roatán. The Garifuna, whose ancestry includes Arawak and Maroons, remained in Punta Gorda, becoming the Bay Island's first permanent post-Columbian settlers. They also migrated from there to parts of the northern coast of Central America, becoming the foundation of the modern-day Garífuna culture in Honduras, Belize and Guatemala.
The majority permanent population of Roatán originated from the Cayman Islands. They arrived in the 1830s shortly after the passage of the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act; the changes in the labour system disrupted the economic structure of the Caymans. The islands had a largely seafaring culture; natives were familiar with the area from turtle fishing and other activities. Former slaveholders from the Cayman Islands were among the first to settle in the seaside locations throughout primarily western Roatán. During the late 1830s and 1840s, former slaves also migrated from the Cayman Islands, in larger number than planters. All together, the former Cayman peoples became the largest cultural group on the island.
For a brief period in the 1850s, Britain declared the Bay Islands its colony. Within a decade, the Crown ceded the territory formally back to Honduras. British colonists were sent to compete for control. They asked American William Walker, a freebooter (filibuster) with a private army, to help end the crisis in 1860 by establishing an independent, English-speaking government over the islands; he eventually fell into the custody of the Honduran government, which executed him.
In the 20th century, there was continued population growth resulting in increased economic changes and environmental challenges. A population boom began with an influx of Spanish-speaking Mestizo migrants from the Honduran mainland. Since the late 20th century, they tripled the previous resident population. Mestizo migrants settled primarily in the urban areas of Coxen Hole and Barrio Los Fuertes (near French Harbour). Even the mainlander influx was dwarfed in number and economic effects by the overwhelming tourist presence in the 21st century. Numerous American,
Canadian, British, New Zealander,
Australian and
South African settlers and entrepreneurs engaged chiefly in the fishing industry, and later, the diving industry, provided the foundation for attracting the tourist trade.
In 1998, Roatán suffered some damage from Hurricane Mitch, temporarily paralysing most commercial activity. The storm also broke up the popular dive-wrecks Aguila and Odyssey.

SARGASSUM:
Represents an immediate
threat to the economics of the Caribbean Islands, the
Gulf of
Mexico, and African West Coast, but is
also a potential asset if it can be economically harvested and used for,
among other things, fertilizer for agriculture: where
there is a world shortage.
BIOMASS - BUILDING
MATERIALS - CANCER
TREATMENTS - CLOTHING
& SHOES - CO2
SEQUESTRATION - COSMETICS
FERTILIZERS - FOODS - MEDICINES - MINERALS - PACKAGING - SUPPLEMENTS - VITAMINS
THE
CARIBBEAN ISLANDS BY
POPULATION
1
Cuba 11,252,999
2 Haiti
11,263,077 (Hispaniola)
3 Dominican Republic 10,766,998 (Hispaniola)
4 Puerto Rico (US) 3,508,000
5 Jamaica 2,729,000
6 Trinidad and Tobago 1,357,000
7 Guadeloupe (France) 405,000
8 Martinique (France) 383,000
9 Bahamas 379,000
10 Barbados 283,000
11 Saint Lucia 172,000
12 Curaçao (Netherlands) 157,000
13 Aruba (Netherlands) 110,000
14 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 110,000
15 United States Virgin Islands
105,000
16 Grenada 104,000
17 Antigua and Barbuda 89,000
18 Dominica 71,000
19 Cayman Islands (UK) 59,000
20 Saint Kitts and Nevis 46,000
21 Sint Maarten (Netherlands) 39,000
22 Turks and Caicos Islands (UK) 37,000
23 Saint Martin (France) 36,000
24 British Virgin Islands (UK) 31,000
25 Caribbean Netherlands
26,000
26 Anguilla (UK) 14,000
27 Saint Barthélemy (France) 10,000
28 Montserrat (UK) 5,000
29
Tortuga 25,936
30
Roatán 110,000
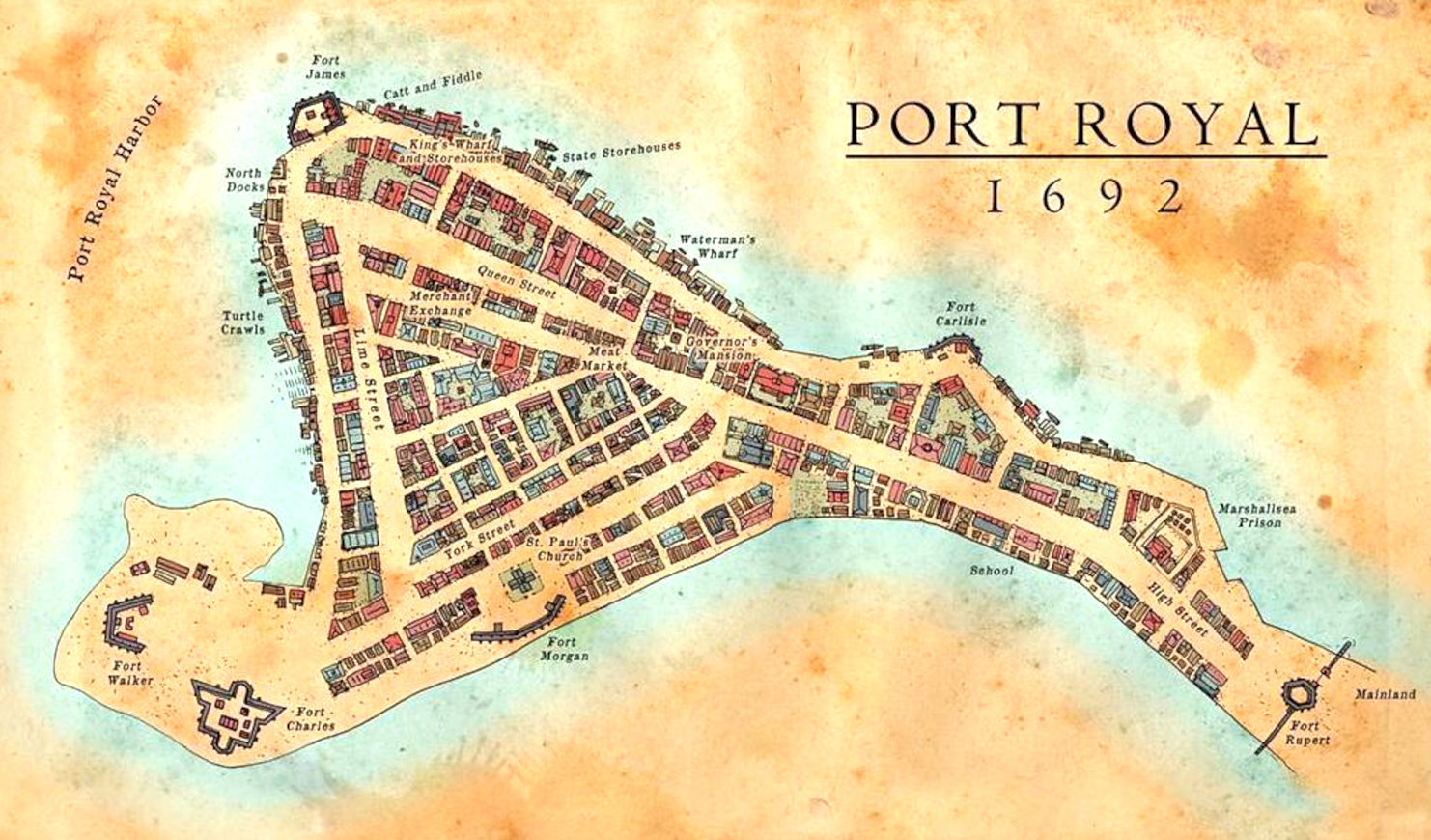
Map
of Port Royal
from 1692, where the notorious buccaneer, Sir Henry Morgan
was buried, along with a Code to give meaning a treasure Map inherited by Lord
Huntington - giving the whereabouts of a Kings ransom. Unfortunately,
Port Royal was sunk when hit by an earthquake and tsunami in June 1692,
along with the grave of the infamous buccaneer, lost in time until
re-discovered by John
Storm and the Elizabeth
Swann. This is the start of a race to find the hidden stash, involving treachery
and industrial espionage.
The
Caribbean
Sea is littered with shipwrecks and dotted with dozens of paradise
islands, where pirates
are said to have buried their treasure.
Many island nations are at risk as to rising
sea levels, caused by climate
change, with the United
Nations powerless to deal with global
warming, being dependent on fossil
fuels. The area has some of the most interesting World
Atlas locations on Planet
Earth.
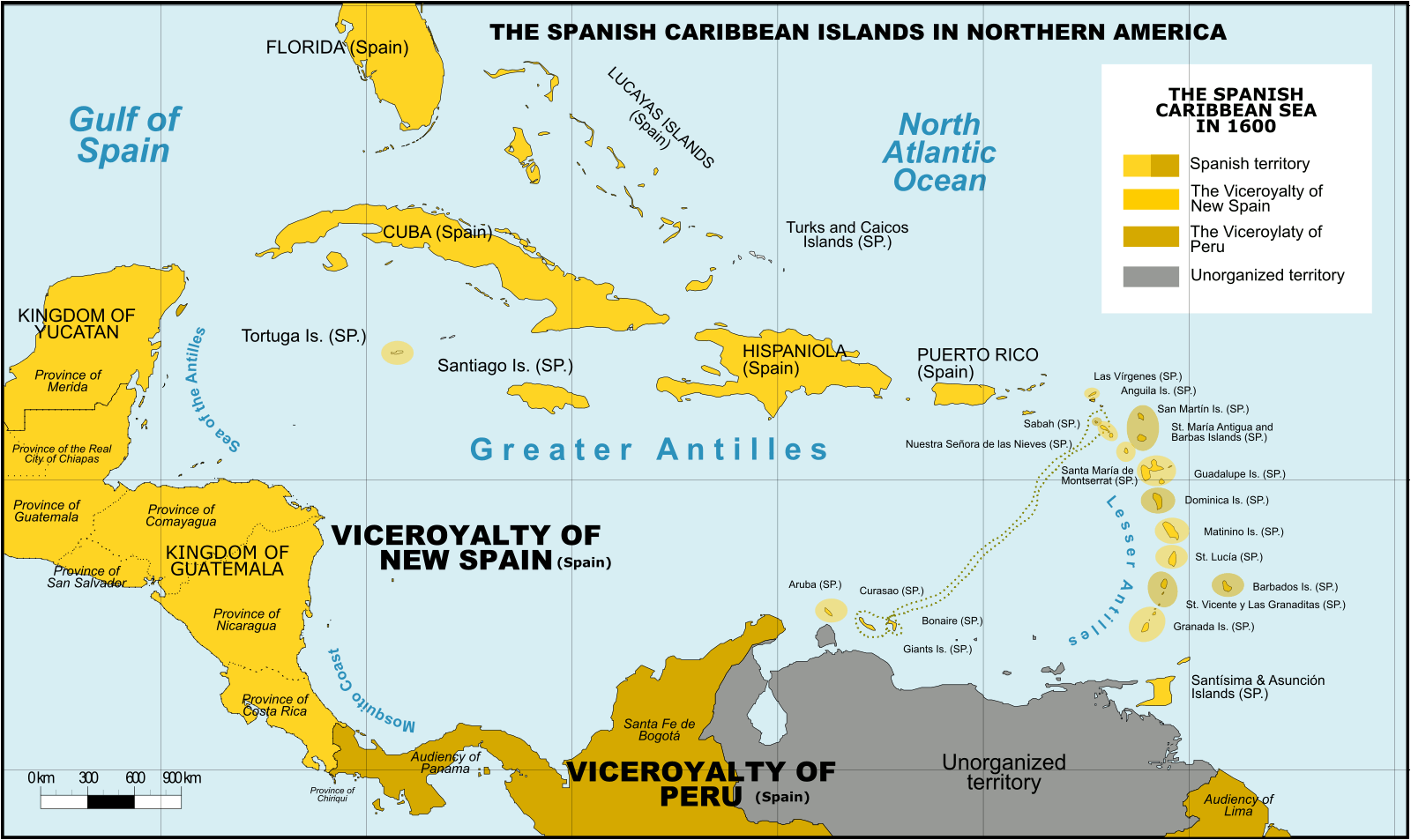
Spanish Caribbean Islands 1600 Spanish Overseas territories Northern America Turks and Caicos Islands (1492-1516, 1516-1678) * Islas Turcas y Caicos The Bahamas (1492-1516, 1516-1648) *Islas Lucayas Bermuda (1503-1516, 1516-1609) *Carabela/Isla de los Diablos Greater Antilles Cuba (1492-1762, 1763-1898) *Juana Cayman Islands (UK) (1503-1670) *Islas de las Tortugas La Española/Hispanola (1492-1795, 1801-1822) Dominican Republic (1492-1795, 1801-1822, 1861-1863) *Santo Domingo Haiti (1492-1793) *Santa María Jamaica (1492-1655) *Isla Santiago Puerto Rico (US) (1493-1898) *San Juan Bautista Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Virgin Islands (1493-1587) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes St. Thomas (US) (1493-1587) St. John (US) (1493-1587) St. Croix (US) (1493-1587) Water Island (US) (1493-1587) British Virgin Islands (UK) (1493-1648) *Islas Once Mil Vírgenes / Islas Vírgenes Tortola (UK) (1493-1648) Virgin Gorda (UK) (1493-1672) Anegada (UK) (1493-1672) Jost Van Dyke (UK) (1493-1672) Anguilla (UK) (1500-1631, 1631-1650) *Isla de la Anguila Saint Martin/Sint Maarten (France/Neth.) (1493-1631) *San Martín Saint-Barthélemy (Fr.) (1493-1648) *San Bartolomeo Saba (Neth.) (1493-1640) *Saba/San Cristóbal Sint Eustatius (Neth.) (1493-1640) *San Eustaquio St. Kitts and Nevis (1493-1628) *Nuestra Señora de las Nieves Saint Kitts (1493-1628) *San Cristóbal Nevis (1493-1628) *Nieves Antigua and Barbuda Barbuda (1493-1628) *Santa Dulcina Antigua (1493-1632) *Santa María de la Antigua Redonda (1493-1632) *Santa María la Redonda Montserrat (UK) (1493-1632) *Santa María de Monstserrat Guadeloupe (Fr.) (1493-1631) *Santa Guadalupe Windward Islands: Dominica (1493-1635) *Domingo Martinique (Fr.) (1502-1635) *Martinino Saint Lucia (St. Lucia) (1502-1660) *Santa Lucía Barbados (1492-1620) *Los Barbados/El Barbudo St. Vincent and the Grenadines (1498-1627) *San Vicente Saint Vincent the Grenadines Grenada (1498-1650) *Concepción Carriacou & Petite Martinique (Grenada) Trinidad & Tobago (1498-1628) *Santísima e Asunción Aruba (Neth.) (1499-1648) *Aruba/Oroba Curaçao (Neth.) (1499-1634) *Curasao/Isla de los Gigantes Bonaire (Neth.) (1499-1635) * Bonaire/Buon Aire Viceroyalty of New Granada Los Roques Archipelago (Ven) La Orchila (Ven) La Tortuga (Ven) La Blanquilla (Ven) Margarita Island (Ven) Coche (Ven) Cubagua (Ven) Other islands (Ven) *Founded Spanish names
CITIES
LOST IN INNERSPACE
ATLANTIS
- MEDITERRANEAN SEA
ATLIT-YAM
- ISRAEL
BAIA
- ITALY
DWARKA
- INDIA
PAVLOPETRI
- GREECE
PHANAGORIA
- BLACK SEA
PORT
ROYAL - JAMAICA
RUNGHOLT
- DENMARK
THONIS-HERACLEION
AND ALEXANDRIA - EGYPT
YONAGUNI
JIMA - JAPAN
ISLAND
NATIONS UNDER THREAT OF SINKING
Cabo
Verde, Republic of
Carteret
Islands
Fiji,
Republic of
Hawaii
Japan
Kiribati
Maldives
Marshall
Islands, Republic of the
Micronesia,
Federated
States of
Palau
Sarichef
Island
Seychelles
Solomon
Islands
Tangier
Island
Torres
Strait Islands
Tuvalu



STUDIO/AGENTS: A draft script for
Kulo-Luna is available on request. Cleopatra The Mummy is currently under
development
|



